Mục lục
Java collection cung cấp Stack class triển khai cấu trúc dữ liệu Stack trong java. Stack là một cấu trúc dữ liệu với nguyên lý cơ bản là vào sau ra trước (Last in First out), ngoài ra Stack class cũng cung cấp các method để thao tác với Stack như pop(), push(), isEmpty() etc.
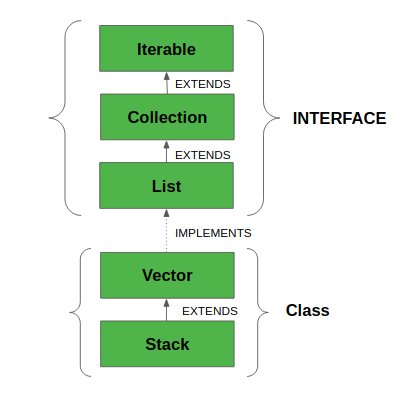
Sơ đồ hệ thống cấp bậc của Stack
Để khởi tạo Stack, chúng ta chỉ có một constructor duy nhất
public Stack()
Ví dụ Stack trong java
import java.io.*;
import java.util.*;
class Test {
// Pushing element on the top of the stack
static void stack_push(Stack<Integer> stack) {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
stack.push(i);
}
}
// Popping element from the top of the stack
static void stack_pop(Stack<Integer> stack) {
System.out.println("Pop :");
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
Integer y = (Integer) stack.pop();
System.out.println(y);
}
}
// Displaying element on the top of the stack
static void stack_peek(Stack<Integer> stack) {
Integer element = (Integer) stack.peek();
System.out.println("Element on stack top : " + element);
}
// Searching element in the stack
static void stack_search(Stack<Integer> stack, int element) {
Integer pos = stack.search(element);
if (pos == -1)
System.out.println("Element not found");
else
System.out.println("Element is found at position " + pos);
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Stack<Integer> stack = new Stack<>();
stack_push(stack);
stack_pop(stack);
stack_push(stack);
stack_peek(stack);
stack_search(stack, 2);
stack_search(stack, 6);
}
}
Output:
Pop :
4
3
2
1
0
Element on stack top : 4
Element is found at position 3
Element not found
Thêm phần tử vào stack
Các phần tử khi được thêm vào Stack sẽ được thêm vào đỉnh của Stack, để thêm phần tử vào Stack chúng ta sử dụng push() method.
Cú pháp
public E push(E item) Parameter: Phần tử có cùng kiểu dữ liệu với Stack Return : Giá trị của phần tử vừa được thêm vào
Ví dụ
import java.util.Stack;
class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating an empty Stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
// Use push() to add elements into the Stack
stack.push("Welcome");
stack.push("To");
stack.push("shareprogramming");
// Displaying the Stack
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + stack);
// Pushing elements into the stack
stack.push("Hello");
stack.push("World");
// Displaying the final Stack
System.out.println("Final Stack: " + stack);
}
}
Output:
Initial Stack: [Welcome, To, shareprogramming]
Final Stack: [Welcome, To, shareprogramming, Hello, World]
Xoá phần tử trong Stack
Khi xoá phần tử trong Stack thì chúng ta chỉ được xoá phần tử từ đỉnh Stack cho đến khi Stack rỗng. Sử dụng pop() để xoá và xem giá trị của phần tử tại đỉnh Stack vừa bị xoá.
Cú pháp
public synchronized E pop() Parameter: Không Return: Phần tử tại đỉnh Stack
Ví dụ
import java.util.Stack;
class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating an empty Stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
// Use push() to add elements into the Stack
stack.push("Welcome");
stack.push("To");
stack.push("shareprogramming");
// Displaying the Stack
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + stack);
System.out.println("Pop: " + stack.pop());
System.out.println("Pop: " + stack.pop());
System.out.println("Final Stack: " + stack);
}
}
Output:
Initial Stack: [Welcome, To, shareprogramming]
Pop: shareprogramming
Pop: To
Final Stack: [Welcome]
Lấy phần tử tại đỉnh Stack
Đôi lúc chúng ta chỉ cần xem giá trị của phần tử tại đỉnh Stack mà không muốn xoá đi chúng, để dụng peek() trong trường hợp này.
Cú pháp
public synchronized E peek() Parameter: Không Return: Phần tử tại đỉnh Stack
Ví dụ
import java.util.Stack;
class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating an empty Stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
// Use push() to add elements into the Stack
stack.push("Welcome");
stack.push("To");
stack.push("shareprogramming");
// Displaying the Stack
System.out.println("Initial Stack: " + stack);
System.out.println("First element: " + stack.peek());
}
}
Output:
Initial Stack: [Welcome, To, shareprogramming]
First element: shareprogramming
Kiểm tra Stack rỗng
empty() method trả về true khi Stack không chứa bất kỳ phần tử nào, ngược lại false.
Cú pháp
Xoá tất cả các phần tử trong Stack
Để xoá tất cả các phần tử trong Stack, sử dụng clear() method. clear() là một supper method của class cha Vector của Stack, giúp xoá toàn bộ các phần tử chứa trong chúng.
Cú pháp
public void clear() Parameter: Không Return: Không
Ví dụ
import java.util.Stack;
class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating an empty Stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("1");
stack.push("1");
stack.push("shareprogramming");
System.out.println("Stack Before clear: " + stack);
stack.clear();
System.out.println("Stack After clear: " + stack);
}
}
Output:
Stack Before clear: [1, 1, shareprogramming]
Stack After clear: []
public boolean empty() Parameter: Không Return: boolean - true nếu Stack rỗng
Ví dụ
import java.util.Stack;
class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating an empty Stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
System.out.println("When Stack is created: " + stack.empty());
stack.push("Welcome");
stack.push("To");
stack.push("shareprogramming");
System.out.println("Stack after add element: " + stack.empty());
}
}
Output:
When Stack is created: true
Stack after add element: false
Tìm kiếm trong Stack
Để tìm kiếm phần tử trong Stack sử dụng search() trả về vị trí đầu tiên xuất hiện phần tử được tìm kiếm, lưu ý nó sẽ tìm kiếm từ đỉnh xuất lui về trước. Trả về -1 nếu không tìm thấy.
Cú pháp
public synchronized int search(Object o) Parameter: Object o cần tìm Return: Vị trí của phần tử tìm thấy or -1
Ví dụ
import java.util.Stack;
class StackDemo {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// Creating an empty Stack
Stack<String> stack = new Stack<>();
stack.push("1");
stack.push("1");
stack.push("shareprogramming");
System.out.println("Does Stack contains 1: " + stack.search("1"));
System.out.println("Does Stack contains haha: " + stack.search("haha"));
}
}
Output:
Does Stack contains 1: 2
Does Stack contains haha: -1
Tóm tắt
Như vậy thì cấu trúc dữ liệu Stack trong java đã được implement sẵn chúng ta chỉ cần biết sử dụng chứ không phải implement lại Stack. Ngoài các method cơ bản thì nó còn có các method hữu ích khác như là kiểm tra Stack rỗng, tìm kiếm etc.
Vì Stack thừa kế từ Vector nên nó cũng sẽ chứa nhiều method cơ bản khác của một Collection như get(int index), clear(), etc.